This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
jin pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/incubator-hugegraph-doc.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 19ea920c doc(ai): sync/merge the ai documentation with README (#375)
19ea920c is described below
commit 19ea920cb110ec7aaff4ed2e9b6450446000d4a9
Author: Hongjun Li <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Wed Nov 6 16:50:18 2024 +0800
doc(ai): sync/merge the ai documentation with README (#375)
Merge the [official
documentation](https://hugegraph.apache.org/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai/)
and the project
[readme](https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai/blob/main/hugegraph-llm/README.md)
---
content/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md | 270 +++++++++++++------------
content/en/docs/images/gradio-kg.png | Bin 246455 -> 3931356 bytes
content/en/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md | 313 ++++++++++++++++-------------
3 files changed, 312 insertions(+), 271 deletions(-)
diff --git a/content/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
b/content/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
index 705b4b14..ba06fe97 100644
--- a/content/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
+++ b/content/cn/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
@@ -9,140 +9,154 @@ hugegraph-ai 旨在探索 HugeGraph 与人工智能(AI)的融合,包括与
的 AI 能力提供全面支持。
### 2 环境要求
-- python 3.8+
-- hugegraph 1.0.0+
+- python 3.9+ (better to use `3.10`)
+- hugegraph-server 1.3+
### 3 准备工作
-- 启动 HugeGraph 数据库,你可以通过 Docker
来实现。请参考这个[链接](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)获取指引。
-- 启动 gradio 交互式 demo,你可以通过以下命令启动,启动后打开
[http://127.0.0.1:8001](http://127.0.0.1:8001)
-```bash
-# ${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR} 为 hugegraph-ai 的根目录,需要自行配置
-export
PYTHONPATH=${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR}/hugegraph-llm/src:${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR}/hugegraph-python-client/src
-python3 ./hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/utils/gradio_demo.py
-```
-- 配置 HugeGraph 数据库连接信息和 LLM 模型信息,可以通过两种方式配置:
- 1. 配置 `./hugegraph-llm/src/config/config.ini` 文件
- 2. 在 gradio 中,分别完成 LLM 和 HugeGraph 的配置后,点击 `Initialize
configs`,将返回初始化后的完整配置文件。如图所示:
- 
-- 离线下载 NLTK stopwords
-```bash
-python3 ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
-```
-
-### 4 使用说明
-#### 4.1 通过 LLM 在 HugeGraph 中构建知识图谱
-##### 4.1.1 通过 gradio 交互式界面构建知识图谱
-- 参数说明:
- - Text: 输入的文本。
- - Schema:接受以下两种类型的文本:
- - 用户定义的 JSON 格式模式。
- - 指定 HugeGraph 图实例的名称,它将自动提取图的模式。
- - Disambiguate word sense:是否进行词义消除歧义。
- - Commit to hugegraph:是否将构建的知识图谱提交到 HugeGraph 服务器
-
-
+1. 启动HugeGraph数据库,可以通过
[Docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)/[Binary
Package](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/download/download/) 运行它。
+
请参阅详细[文档](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)以获取更多指导
+2. 克隆项目
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
+ ```
+3. 安装 [hugegraph-python-client](../hugegraph-python-client) 和
[hugegraph_llm](src/hugegraph_llm)
+ ```bash
+ cd ./incubator-hugegraph-ai # better to use virtualenv (source
venv/bin/activate)
+ pip install ./hugegraph-python-client
+ pip install -r ./hugegraph-llm/requirements.txt
+ ```
+4. 进入项目目录
+ ```bash
+ cd ./hugegraph-llm/src
+ ```
+5. 启动 **Graph RAG** 的 gradio 交互 demo,可以使用以下命令运行,启动后打开 http://127.0.0.1:8001
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app
+ ```
+ 默认主机为 `0.0.0.0` ,端口为 `8001` 。您可以通过传递命令行参数 `--host` 和 `--port` 来更改它们。
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 18001
+ ```
+6. 启动 **Text2Gremlin** 的 gradio 交互演示,可以使用以下命令运行,启动后打开 http://127.0.0.1:8002
,您还可以按上述方式更改默认主机 `0.0.0.0` 和端口 `8002` 。(🚧ing)
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.gremlin_generate_web_demo
+ ```
+7. 在运行演示程序后,配置文件文件将被删除。`.env ` 将自动生成在 `hugegraph-llm/.env` 路径下。此外,还有一个与 prompt
相关的配置文件 `config_prompt.yaml`
。也会在`hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yaml`路径下生成。
+ 您可以在页面上修改内容,触发相应功能后会自动保存到配置文件中。你也可以直接修改文件而无需重启应用程序;只需刷新页面即可加载最新的更改。
+ (可选)要重新生成配置文件,您可以将 `config.generate` 与 `-u` 或 `--update` 一起使用。
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.config.generate --update
+ ```
+8. (**可选**)您可以使用
[hugegraph-hubble](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-hubble/#21-use-docker-convenient-for-testdev)
来访问图形数据,可以通过
[Docker/Docker-Compose](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hubble) 运行它以获得指导。
(Hubble 是一个图形分析仪表板,包括数据加载/模式管理/图形遍历/显示)。
+9. (__可选__)离线下载 NLTK 停用词
+ ```bash
+ python ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
+ ```
+
+## 4 示例
+### 4.1 通过 LLM 在 HugeGraph 中构建知识图谱
+#### 4.1.1 通过 gradio 交互式界面构建知识图谱
+
+**参数描述:**
+
+- Docs:
+ - text: 从纯文本建立 rag 索引
+ - file: 上传文件:<u>TXT</u> 或 <u>.docx</u>(可同时选择多个文件)
+-
[Schema](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/clients/restful-api/schema/):(接受**2种类型**)
+ - 用户定义模式( JSON
格式,遵循[模板](https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai/blob/aff3bbe25fa91c3414947a196131be812c20ef11/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/config/config_data.py#L125)来修改它)
+ - 指定 HugeGraph 图实例的名称,它将自动从中获取模式(如 **“hugegraph”**)
+- Graph extract head: 用户自定义的图提取提示
+- 如果已经存在图数据,你应该点击 "**Rebuild vid Index**" 来更新索引
+
+
+
##### 4.1.2 通过代码构建知识图谱
-- 完整代码
-```python
-from hugegraph_llm.llms.init_llm import LLMs
-from hugegraph_llm.operators.kg_construction_task import KgBuilder
-
-llm = LLMs().get_llm()
-builder = KgBuilder(llm)
-(
- builder
- .import_schema(from_hugegraph="test_graph").print_result()
- .extract_triples(TEXT).print_result()
- .disambiguate_word_sense().print_result()
- .commit_to_hugegraph()
- .run()
-)
-```
-- 时序图
-
-
-1. 初始化:初始化 LLMs 实例,获取 LLM,然后创建图谱构建的任务实例 `KgBuilder`,KgBuilder 中定义了多个
operator,用户可以根据需求自由组合达到目的。(tip: `print_result()` 可以在控制台打印每一步输出的结果,不影响整体执行逻辑)
-
-```python
-llm = LLMs().get_llm()
-builder = KgBuilder(llm)
-```
-
-2. 导入 Schema:使用 `import_schema` 方法导入,支持三种模式:
- - 从 HugeGraph 实例导入,指定 HugeGraph 图实例的名称,它将自动提取图的模式。
- - 从用户定义的模式导入,接受用户定义的 JSON 格式模式。
- - 从提取结果导入(即将发布)
-```python
-# Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
-builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="test_graph").print_result()
-# Import schema from user-defined schema
-builder.import_schema(from_user_defined="xxx").print_result()
-# Import schema from an extraction result
-builder.import_schema(from_extraction="xxx").print_result()
-```
-3. 提取三元组:使用 `extract_triples` 方法从文本中提取三元组。
-
-```python
-TEXT = "Meet Sarah, a 30-year-old attorney, and her roommate, James, whom
she's shared a home with since 2010."
-builder.extract_triples(TEXT).print_result()
-```
-4. 消除词义歧义:使用 `disambiguate_word_sense` 方法消除词义歧义。
-
-```python
-builder.disambiguate_word_sense().print_result()
-```
-5. 提交到 HugeGraph:使用 `commit_to_hugegraph` 方法提交构建的知识图谱到 HugeGraph 实例。
-
-```python
-builder.commit_to_hugegraph().print_result()
-```
-6. 运行:使用 `run` 方法执行上述操作。
-```python
-builder.run()
-```
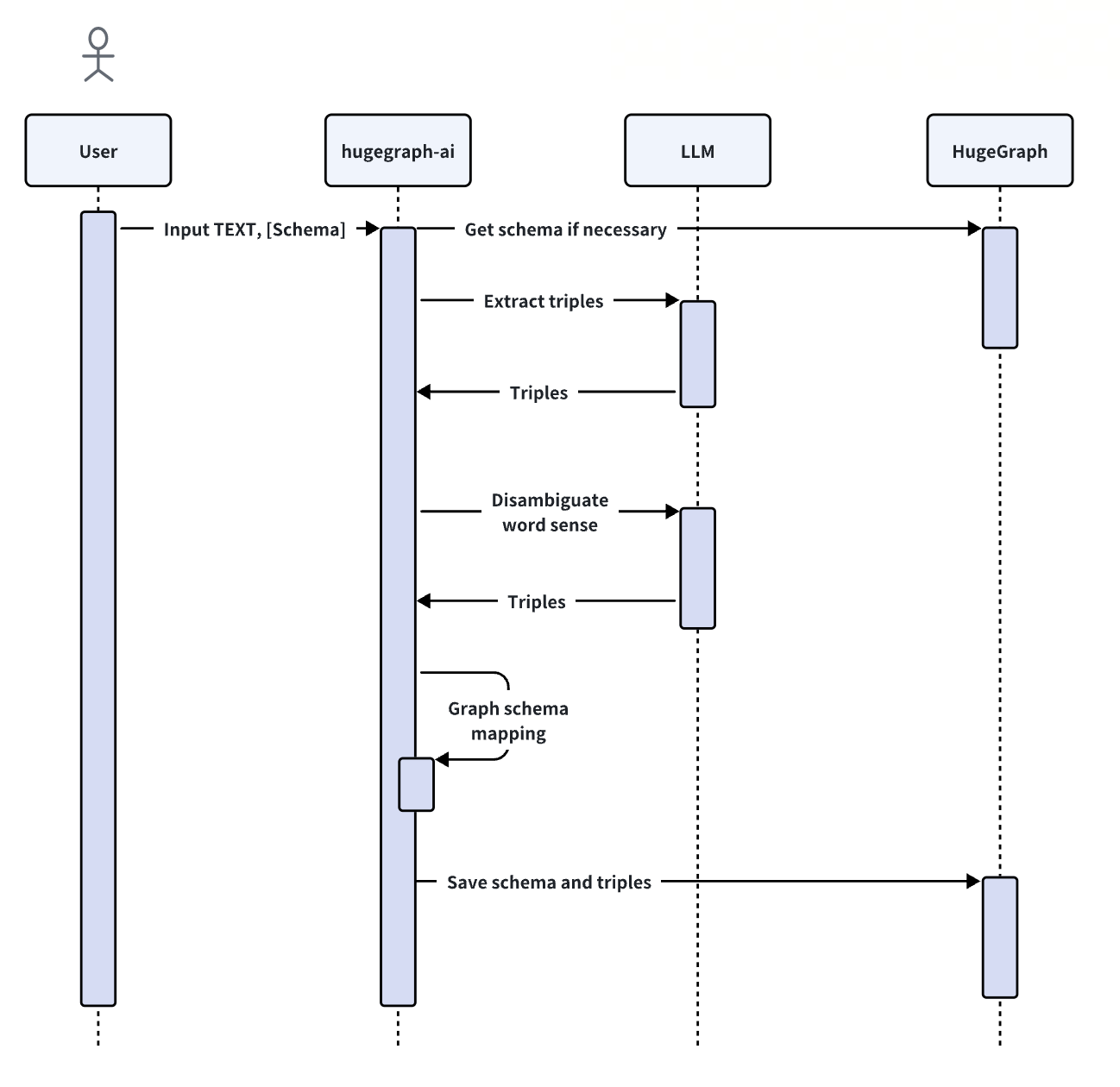
+`KgBuilder` 类用于构建知识图谱。下面是使用过程:
+
+1. **初始化**: `KgBuilder` 类使用语言模型的实例进行初始化。这可以从 `LLMs` 类中获得。
+ 初始化 `LLMs`实例,获取 `LLM`,然后创建一个任务实例 `KgBuilder` 用于图的构建。`KgBuilder`
定义了多个运算符,用户可以根据需要自由组合它们。(提示:`print_result()` 可以在控制台中打印出每一步的结果,而不会影响整个执行逻辑)
+ ```python
+ from hugegraph_llm.models.llms.init_llm import LLMs
+ from hugegraph_llm.operators.kg_construction_task import KgBuilder
+
+ TEXT = ""
+ builder = KgBuilder(LLMs().get_llm())
+ (
+ builder
+ .import_schema(from_hugegraph="talent_graph").print_result()
+ .chunk_split(TEXT).print_result()
+ .extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ .commit_to_hugegraph()
+ .run()
+ )
+ ```
+ 
+2. **导入架构**: `import_schema` 方法用于从源导入架构。源可以是 HugeGraph 实例、用户定义的模式或提取结果。可以链接
`print_result` 方法来打印结果。
+ ```python
+ # Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
+ builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="xxx").print_result()
+ # Import schema from an extraction result
+ builder.import_schema(from_extraction="xxx").print_result()
+ # Import schema from user-defined schema
+ builder.import_schema(from_user_defined="xxx").print_result()
+ ```
+3. **Chunk Split** : `chunk_split` 方法用于将输入文本分割为块。文本应该作为字符串参数传递给方法。
+ ```python
+ # Split the input text into documents
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="document").print_result()
+ # Split the input text into paragraphs
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="paragraph").print_result()
+ # Split the input text into sentences
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="sentence").print_result()
+ ```
+4. **信息抽取**:`extract_info` 方法用于从文本中提取信息。文本应该作为字符串参数传递给方法。
+ ```python
+ TEXT = "Meet Sarah, a 30-year-old attorney, and her roommate, James, whom
she's shared a home with since 2010."
+ # extract property graph from the input text
+ builder.extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ # extract triples from the input text
+ builder.extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ ```
+5. **Commit to HugeGraph** : `commit_to_hugegraph` 方法用于将构建的知识图谱提交到 HugeGraph
实例。
+ ```python
+ builder.commit_to_hugegraph().print_result()
+ ```
+6. **Run** : `run` 方法用于执行链式操作。
+ ```python
+ builder.run()
+ ```
+ `KgBuilder` 类的方法可以链接在一起以执行一系列操作。
#### 4.2 基于 HugeGraph 的检索增强生成(RAG)
-##### 4.1.1 通过 gradio 交互问答
-1. 首先点击 `Initialize HugeGraph test data` 按钮,初始化 HugeGraph 数据。
- 
-2. 然后点击 `Retrieval augmented generation` 按钮,生成问题的答案。
- 
-##### 4.1.2 通过代码构建 Graph RAG
-- 完整代码
-```python
-graph_rag = GraphRAG()
-result = (
- graph_rag.extract_keyword(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
- .query_graph_for_rag(
- max_deep=2,
- max_items=30
- ).print_result()
- .synthesize_answer().print_result()
- .run(verbose=True)
-)
-```
-1. extract_keyword: 提取关键词, 并进行近义词扩展
-```python
-graph_rag.extract_keyword(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
-```
-2. query_graph_for_rag: 从 HugeGraph 中检索对应的关键词,及其多度的关联关系
- - max_deep: hugegraph 检索的最大深度
- - max_items: hugegraph 最大返回结果数
-```python
-graph_rag.query_graph_for_rag(
- max_deep=2,
- max_items=30
-).print_result()
-```
-3. synthesize_answer: 针对提问,汇总结果,组织语言回答问题。
-```python
-graph_rag.synthesize_answer().print_result()
-```
-4. run: 执行上述操作。
-```python
-graph_rag.run(verbose=True)
-```
+`RAGPipeline` 类用于将 HugeGraph 与大型语言模型集成,以提供检索增强生成功能。下面是使用过程:
+
+1. **提取关键字**:提取关键字并扩展同义词。
+ ```python
+ from hugegraph_llm.operators.graph_rag_task import RAGPipeline
+ graph_rag = RAGPipeline()
+ graph_rag.extract_keywords(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
+ ```
+2. **根据关键字匹配 Vid**::将节点与图中的关键字匹配。
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.keywords_to_vid().print_result()
+ ```
+3. **RAG 的查询图**:从 HugeGraph 中检索对应的关键词及其多度关联关系。
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.query_graphdb(max_deep=2, max_items=30).print_result()
+ ```
+4. **重新排序搜索结果**:根据问题与结果之间的相似性对搜索结果进行重新排序。
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.merge_dedup_rerank().print_result()
+ ```
+5. **合成答案**:总结结果并组织语言来回答问题。
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.synthesize_answer(vector_only_answer=False,
graph_only_answer=True).print_result()
+ ```
+6. **运行**:`run` 方法用于执行上述操作。
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.run(verbose=True)
+ ```
diff --git a/content/en/docs/images/gradio-kg.png
b/content/en/docs/images/gradio-kg.png
index 9e80b28d..825c1933 100644
Binary files a/content/en/docs/images/gradio-kg.png and
b/content/en/docs/images/gradio-kg.png differ
diff --git a/content/en/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
b/content/en/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
index d0751b29..b6efc63a 100644
--- a/content/en/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
+++ b/content/en/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-ai.md
@@ -4,149 +4,176 @@ linkTitle: "Explore with HugeGraph-AI"
weight: 4
---
-### 1 HugeGraph-AI Overview
+## 1 HugeGraph-AI Overview
hugegraph-ai aims to explore the integration of HugeGraph and artificial
intelligence (AI), including applications combined
with large models, integration with graph machine learning components, etc.,
to provide comprehensive support for developers to use HugeGraph's AI
capabilities in projects.
-### 2 Environment Requirements
-- python 3.8+
-- hugegraph 1.0.0+
-
-### 3 Preparation
-- Start the HugeGraph database, you can achieve this through Docker. Please
refer to this [link](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph) for guidance.
-- Start the gradio interactive demo, you can start with the following command,
and open [http://127.0.0.1:8001](http://127.0.0.1:8001) after starting
-
-```bash
-# ${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR} is the root directory of hugegraph-ai, which needs to be
configured by yourself
-export
PYTHONPATH=${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR}/hugegraph-llm/src:${PROJECT_ROOT_DIR}/hugegraph-python-client/src
-python3 ./hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/utils/gradio_demo.py
-```
-- Configure HugeGraph database connection information and LLM information,
which can be configured in two ways:
- 1. Configure the `./hugegraph-llm/src/config/config.ini` file
- 2. In gradio, after completing the configurations for LLM and HugeGraph,
click on `Initialize configs`, the complete and initialized configuration file
will be outputted.
- 
-- offline download NLTK stopwords
-```bash
-python3 ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
-```
-
-### 4 How to use
-#### 4.1 Build a knowledge graph in HugeGraph through LLM
-##### 4.1.1 Build a knowledge graph through the gradio interactive interface
-- Parameter description:
- - Text: The input text.
- - Schema: Accepts the following two types of text:
- - User-defined JSON format schema.
- - Specify the name of the HugeGraph graph instance, which will
automatically extract the schema of the graph.
- - Disambiguate word sense: Whether to disambiguate word sense.
- - Commit to hugegraph: Whether to submit the constructed knowledge graph to
the HugeGraph server
-
-
-
-##### 4.1.2 Build a knowledge graph through code
-- Complete code
-```python
-from hugegraph_llm.llms.init_llm import LLMs
-from hugegraph_llm.operators.kg_construction_task import KgBuilder
-
-llm = LLMs().get_llm()
-builder = KgBuilder(llm)
-(
- builder
- .import_schema(from_hugegraph="test_graph").print_result()
- .extract_triples(TEXT).print_result()
- .disambiguate_word_sense().print_result()
- .commit_to_hugegraph()
- .run()
-)
-```
-- Sequence Diagram
- 
-
-1. Initialize: Initialize the LLMs instance, get the LLM, and then create a
task instance `KgBuilder` for graph construction. `KgBuilder` defines multiple
operators, and users can freely combine them according to their needs. (tip:
`print_result()` can print the result of each step in the console, without
affecting the overall execution logic)
-
-```python
-llm = LLMs().get_llm()
-builder = KgBuilder(llm)
-```
-2. Import Schema: Import using the `import_schema` method, which supports
three modes:
- - Import from a HugeGraph instance, specify the name of the HugeGraph
graph instance, and it will automatically extract the schema of the graph.
- - Import from a user-defined schema, accept user-defined JSON format
schema.
- - Import from the extraction result (release soon)
-
-```python
-# Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
-builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="test_graph").print_result()
-# Import schema from user-defined schema
-builder.import_schema(from_user_defined="xxx").print_result()
-# Import schema from an extraction result
-builder.import_schema(from_extraction="xxx").print_result()
-```
-3. Extract triples: Use the `extract_triples` method to extract triples from
the text.
-
-```python
-TEXT = "Meet Sarah, a 30-year-old attorney, and her roommate, James, whom
she's shared a home with since 2010."
-builder.extract_triples(TEXT).print_result()
-```
-4. Disambiguate word sense: Use the `disambiguate_word_sense` method to
disambiguate word sense.
-
-```python
-builder.disambiguate_word_sense().print_result()
-```
-5. Commit to HugeGraph: Use the `commit_to_hugegraph` method to submit the
constructed knowledge graph to the HugeGraph instance.
-
-```python
-builder.commit_to_hugegraph().print_result()
-```
-
-6. Run: Use the `run` method to execute the above operations.
-
-```python
-builder.run()
-```
-
-#### 4.2 Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) based on HugeGraph
-##### 4.1.1 Interactive Q&A through gradio
-1. First click the `Initialize HugeGraph test data` button to initialize the
HugeGraph data.
- 
-2. Then click the `Retrieval augmented generation` button to generate the
answer to the question.
- 
-
-##### 4.1.2 Build Graph RAG through code
-- code
-```python
-graph_rag = GraphRAG()
-result = (
- graph_rag.extract_keyword(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
- .query_graph_for_rag(
- max_deep=2,
- max_items=30
- ).print_result()
- .synthesize_answer().print_result()
- .run(verbose=True)
-)
-```
-1. extract_keyword: Extract keywords and expand synonyms.
-
-```python
-graph_rag.extract_keyword(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
-```
-2. query_graph_for_rag: Retrieve the corresponding keywords and their
multi-degree associated relationships from HugeGraph.
- - max_deep: The maximum depth of hugegraph retrieval.
- - max_items: The maximum number of results returned by hugegraph.
-
-```python
-graph_rag.query_graph_for_rag(
- max_deep=2,
- max_items=30
-).print_result()
-```
-3. synthesize_answer: Summarize the results and organize the language to
answer the question.
-```python
-graph_rag.synthesize_answer().print_result()
-```
-4. run: Execute the above operations.
-
-```python
-graph_rag.run(verbose=True)
-```
+## 2 Environment Requirements
+- python 3.9+
+- hugegraph-server 1.2+
+
+## 3 Preparation
+
+1. Start the HugeGraph database, you can run it via
[Docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)/[Binary
Package](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/download/download/).
+ Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)
for more guidance
+
+2. Clone this project
+ ```bash
+ git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
+ ```
+
+3. Install [hugegraph-python-client](../hugegraph-python-client) and
[hugegraph_llm](src/hugegraph_llm)
+ ```bash
+ cd ./incubator-hugegraph-ai # better to use virtualenv (source
venv/bin/activate)
+ pip install ./hugegraph-python-client
+ pip install -r ./hugegraph-llm/requirements.txt
+ ```
+
+4. Enter the project directory
+ ```bash
+ cd ./hugegraph-llm/src
+ ```
+
+5. Start the gradio interactive demo of **Graph RAG**, you can run with the
following command, and open http://127.0.0.1:8001 after starting
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app
+ ```
+ The default host is `0.0.0.0` and the port is `8001`. You can change them
by passing command line arguments`--host` and `--port`.
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 18001
+ ```
+
+6. Or start the gradio interactive demo of **Text2Gremlin**, you can run with
the following command, and open http://127.0.0.1:8002 after starting. You can
also change the default host `0.0.0.0` and port `8002` as above. (🚧ing)
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.gremlin_generate_web_demo
+ ```
+
+7. After running the web demo, the config file `.env` will be automatically
generated at the path `hugegraph-llm/.env`. Additionally, a prompt-related
configuration file `config_prompt.yaml` will also be generated at the path
`hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yaml`.
+
+ You can modify the content on the web page, and it will be automatically
saved to the configuration file after the corresponding feature is triggered.
You can also modify the file directly without restarting the web application;
simply refresh the page to load your latest changes.
+
+ (Optional)To regenerate the config file, you can use `config.generate`
with `-u` or `--update`.
+ ```bash
+ python3 -m hugegraph_llm.config.generate --update
+ ```
+
+8. (__Optional__) You could use
+
[hugegraph-hubble](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-hubble/#21-use-docker-convenient-for-testdev)
+ to visit the graph data, could run it via
[Docker/Docker-Compose](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hubble)
+ for guidance. (Hubble is a graph-analysis dashboard include data
loading/schema management/graph traverser/display).
+
+9. (__Optional__) offline download NLTK stopwords
+ ```bash
+ python ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
+ ```
+
+
+## 4 Examples
+### 4.1 Build a knowledge graph in HugeGraph through LLM
+#### 4.1.1 Build a knowledge graph through the gradio interactive interface
+
+**Parameter description:**
+
+- Docs:
+ - text: Build rag index from plain text
+ - file: Upload file(s) which should be <u>TXT</u> or <u>.docx</u> (Multiple
files can be selected together)
+- [Schema](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/clients/restful-api/schema/):
(Accept **2 types**)
+ - User-defined Schema (JSON format, follow the
[template](https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai/blob/aff3bbe25fa91c3414947a196131be812c20ef11/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/config/config_data.py#L125)
+ to modify it)
+ - Specify the name of the HugeGraph graph instance, it will automatically
get the schema from it (like
+ **"hugegraph"**)
+- Graph extract head: The user-defined prompt of graph extracting
+- If already exist the graph data, you should click "**Rebuild vid Index**" to
update the index
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Build a knowledge graph through code
+
+The `KgBuilder` class is used to construct a knowledge graph. Here is a brief
usage guide:
+
+1. **Initialization**: The `KgBuilder` class is initialized with an instance
of a language model.
+This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
+ Initialize the LLMs instance, get the LLM, and then create a task instance
`KgBuilder` for graph construction. `KgBuilder` defines multiple operators, and
users can freely combine them according to their needs. (tip: `print_result()`
can print the result of each step in the console, without affecting the overall
execution logic)
+ ```python
+ from hugegraph_llm.models.llms.init_llm import LLMs
+ from hugegraph_llm.operators.kg_construction_task import KgBuilder
+
+ TEXT = ""
+ builder = KgBuilder(LLMs().get_llm())
+ (
+ builder
+ .import_schema(from_hugegraph="talent_graph").print_result()
+ .chunk_split(TEXT).print_result()
+ .extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ .commit_to_hugegraph()
+ .run()
+ )
+ ```
+ 
+2. **Import Schema**: The `import_schema` method is used to import a schema
from a source. The source can be a HugeGraph instance, a user-defined schema or
an extraction result. The method `print_result` can be chained to print the
result.
+ ```python
+ # Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
+ builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="xxx").print_result()
+ # Import schema from an extraction result
+ builder.import_schema(from_extraction="xxx").print_result()
+ # Import schema from user-defined schema
+ builder.import_schema(from_user_defined="xxx").print_result()
+ ```
+3. **Chunk Split**: The `chunk_split` method is used to split the input text
into chunks. The text should be passed as a string argument to the method.
+ ```python
+ # Split the input text into documents
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="document").print_result()
+ # Split the input text into paragraphs
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="paragraph").print_result()
+ # Split the input text into sentences
+ builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="sentence").print_result()
+ ```
+4. **Extract Info**: The `extract_info` method is used to extract info from a
text. The text should be passed as a string argument to the method.
+ ```python
+ TEXT = "Meet Sarah, a 30-year-old attorney, and her roommate, James, whom
she's shared a home with since 2010."
+ # extract property graph from the input text
+ builder.extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ # extract triples from the input text
+ builder.extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
+ ```
+5. **Commit to HugeGraph**: The `commit_to_hugegraph` method is used to commit
the constructed knowledge graph to a HugeGraph instance.
+ ```python
+ builder.commit_to_hugegraph().print_result()
+ ```
+6. **Run**: The `run` method is used to execute the chained operations.
+ ```python
+ builder.run()
+ ```
+ The methods of the `KgBuilder` class can be chained together to perform a
sequence of operations.
+
+### 4.2 Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) based on HugeGraph
+
+The `RAGPipeline` class is used to integrate HugeGraph with large language
models to provide retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
+Here is a brief usage guide:
+
+1. **Extract Keyword**: Extract keywords and expand synonyms.
+ ```python
+ from hugegraph_llm.operators.graph_rag_task import RAGPipeline
+ graph_rag = RAGPipeline()
+ graph_rag.extract_keywords(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
+ ```
+2. **Match Vid from Keywords**: Match the nodes with the keywords in the graph.
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.keywords_to_vid().print_result()
+ ```
+3. **Query Graph for Rag**: Retrieve the corresponding keywords and their
multi-degree associated relationships from HugeGraph.
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.query_graphdb(max_deep=2, max_items=30).print_result()
+ ```
+4. **Rerank Searched Result**: Rerank the searched results based on the
similarity between the question and the results.
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.merge_dedup_rerank().print_result()
+ ```
+5. **Synthesize Answer**: Summarize the results and organize the language to
answer the question.
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.synthesize_answer(vector_only_answer=False,
graph_only_answer=True).print_result()
+ ```
+6. **Run**: The `run` method is used to execute the above operations.
+ ```python
+ graph_rag.run(verbose=True)
+ ```
