This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
jin pushed a commit to branch main
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/main by this push:
new f20afaf docs(llm): update configuration file related (#99)
f20afaf is described below
commit f20afafd287b5bc534423f3bd45519946e00ad1e
Author: Hongjun Li <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Wed Nov 6 16:58:48 2024 +0800
docs(llm): update configuration file related (#99)
1. Add prompt configuration file description
2. Add a description of where the `.env` and prompt configuration files are
located
3. The images use the schematics in the
[hg-doc](https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-doc/tree/master/content/en/docs/images)
repository
This is because the two documents are initially determined to be
unified in content, so for the same pictures involved in the two documents, it
is considered to use the pictures of the same warehouse for display, rather
than maintaining two pictures in two different warehouses
---------
Co-authored-by: imbajin <[email protected]>
Co-authored-by: vichayturen <[email protected]>
---
hugegraph-llm/README.md | 88 ++++++++++++++++++++++++-------------------------
1 file changed, 43 insertions(+), 45 deletions(-)
diff --git a/hugegraph-llm/README.md b/hugegraph-llm/README.md
index eeb7f43..e9d6f90 100644
--- a/hugegraph-llm/README.md
+++ b/hugegraph-llm/README.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# hugegraph-llm
-## Summary
+## 1. Summary
The `hugegraph-llm` is a tool for the implementation and research related to
large language models.
This project includes runnable demos, it can also be used as a third-party
library.
@@ -15,15 +15,15 @@ graph systems and large language models.
2. Use natural language to operate graph databases (Gremlin/Cypher)
3. Knowledge graph supplements answer context (GraphRAG)
-## Environment Requirements
+## 2. Environment Requirements
-- python 3.9+
-- hugegraph-server 1.2+
+- python 3.9+ (better to use `3.10`)
+- hugegraph-server 1.3+
-## Preparation
+## 3. Preparation
-1. Start the HugeGraph database, you can run it via
[Docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)/[Binary
Package](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/download/download/).
-Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)
for more guidance (PS: Graph visualization in step8)
+1. Start the HugeGraph database, you can run it via
[Docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)/[Binary
Package](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/download/download/).
+ Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)
for more guidance
2. Clone this project
```bash
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
@@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-s
```bash
cd ./hugegraph-llm/src
```
-
5. Start the gradio interactive demo of **Graph RAG**, you can run with the
following command, and open http://127.0.0.1:8001 after starting
```bash
python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app
@@ -47,33 +46,53 @@ Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-s
```bash
python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 18001
```
-
6. Or start the gradio interactive demo of **Text2Gremlin**, you can run with
the following command, and open http://127.0.0.1:8002 after starting. You can
also change the default host `0.0.0.0` and port `8002` as above. (🚧ing)
```bash
python3 -m hugegraph_llm.demo.gremlin_generate_web_demo
```
-
-7. After running the web demo, the config file `.env` will be automatically
generated. You can modify its content on the web page. Or modify the file
directly and restart the web application.
-
- (Optional)To regenerate the config file, you can use `config.generate`
with `-u` or `--update`.
+7. After running the web demo, the config file `.env` will be automatically
generated at the path `hugegraph-llm/.env`. Additionally, a prompt-related
configuration file `config_prompt.yaml` will also be generated at the path
`hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yaml`.
+ You can modify the content on the web page, and it will be automatically
saved to the configuration file after the corresponding feature is triggered.
You can also modify the file directly without restarting the web application;
simply refresh the page to load your latest changes.
+ (Optional)To regenerate the config file, you can use `config.generate`
with `-u` or `--update`.
```bash
python3 -m hugegraph_llm.config.generate --update
```
-
8. (__Optional__) You could use
-[hugegraph-hubble](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-hubble/#21-use-docker-convenient-for-testdev)
-to visit the graph data, could run it via
[Docker/Docker-Compose](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hubble)
-for guidance. (Hubble is a graph-analysis dashboard include data
loading/schema management/graph traverser/display).
+
[hugegraph-hubble](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-hubble/#21-use-docker-convenient-for-testdev)
+ to visit the graph data, could run it via
[Docker/Docker-Compose](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hubble)
+ for guidance. (Hubble is a graph-analysis dashboard include data
loading/schema management/graph traverser/display).
+9. (__Optional__) offline download NLTK stopwords
+ ```bash
+ python ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
+ ```
+
+## 4 Examples
+
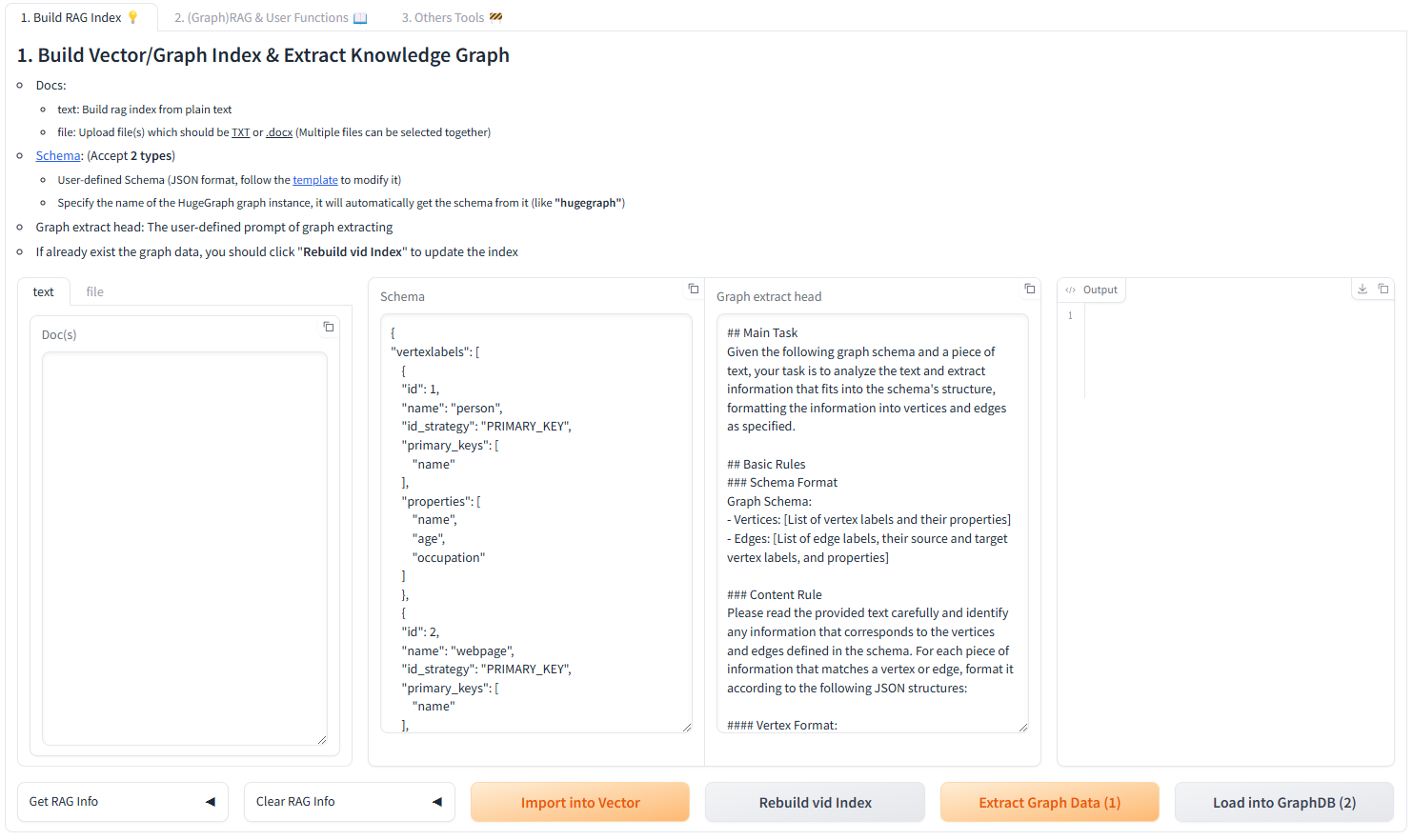
+### 4.1 Build a knowledge graph in HugeGraph through LLM
+#### 4.1.1 Build a knowledge graph through the gradio interactive interface
-## Examples
+**Parameter description:**
-### 1.Build a knowledge graph in HugeGraph through LLM
+- Docs:
+ - text: Build rag index from plain text
+ - file: Upload file(s) which should be <u>TXT</u> or <u>.docx</u> (Multiple
files can be selected together)
+- [Schema](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/clients/restful-api/schema/):
(Accept **2 types**)
+ - User-defined Schema (JSON format, follow the
[template](https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai/blob/aff3bbe25fa91c3414947a196131be812c20ef11/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/config/config_data.py#L125)
+ to modify it)
+ - Specify the name of the HugeGraph graph instance, it will automatically
get the schema from it (like
+ **"hugegraph"**)
+- Graph extract head: The user-defined prompt of graph extracting
+- If already exist the graph data, you should click "**Rebuild vid Index**" to
update the index
+
+
+
+#### 4.1.2 Build a knowledge graph through code
The `KgBuilder` class is used to construct a knowledge graph. Here is a brief
usage guide:
1. **Initialization**: The `KgBuilder` class is initialized with an instance
of a language model.
-This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
+This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
+ Initialize the LLMs instance, get the LLM, and then create a task instance
`KgBuilder` for graph construction. `KgBuilder` defines multiple operators, and
users can freely combine them according to their needs. (tip: `print_result()`
can print the result of each step in the console, without affecting the overall
execution logic)
```python
from hugegraph_llm.models.llms.init_llm import LLMs
@@ -90,9 +109,8 @@ This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
.run()
)
```
-
+ 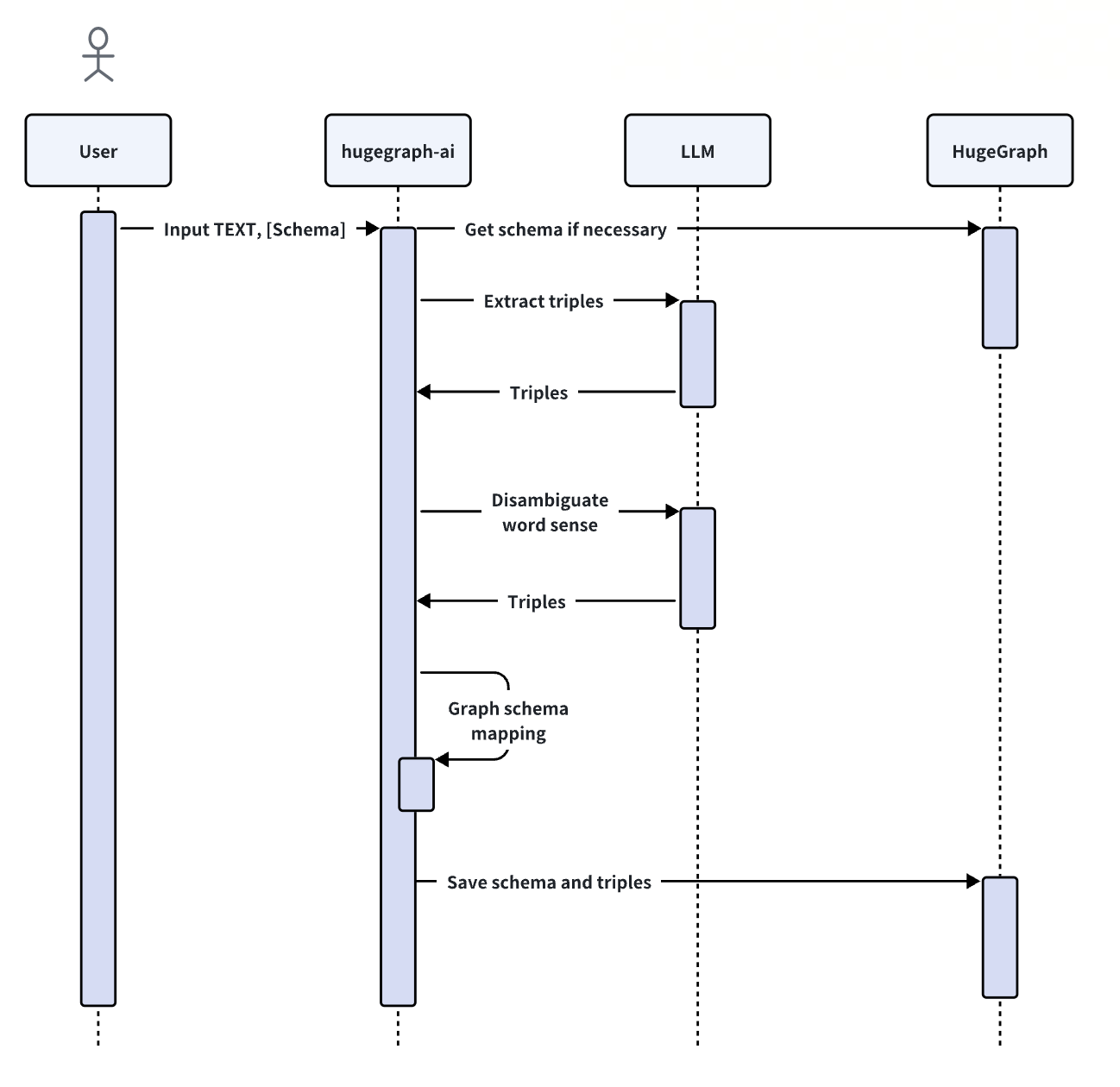
2. **Import Schema**: The `import_schema` method is used to import a schema
from a source. The source can be a HugeGraph instance, a user-defined schema or
an extraction result. The method `print_result` can be chained to print the
result.
-
```python
# Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="xxx").print_result()
@@ -101,9 +119,7 @@ This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
# Import schema from user-defined schema
builder.import_schema(from_user_defined="xxx").print_result()
```
-
3. **Chunk Split**: The `chunk_split` method is used to split the input text
into chunks. The text should be passed as a string argument to the method.
-
```python
# Split the input text into documents
builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="document").print_result()
@@ -112,9 +128,7 @@ This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
# Split the input text into sentences
builder.chunk_split(TEXT, split_type="sentence").print_result()
```
-
4. **Extract Info**: The `extract_info` method is used to extract info from a
text. The text should be passed as a string argument to the method.
-
```python
TEXT = "Meet Sarah, a 30-year-old attorney, and her roommate, James, whom
she's shared a home with since 2010."
# extract property graph from the input text
@@ -122,60 +136,44 @@ This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
# extract triples from the input text
builder.extract_info(extract_type="property_graph").print_result()
```
-
5. **Commit to HugeGraph**: The `commit_to_hugegraph` method is used to commit
the constructed knowledge graph to a HugeGraph instance.
-
```python
builder.commit_to_hugegraph().print_result()
```
-
6. **Run**: The `run` method is used to execute the chained operations.
-
```python
builder.run()
```
+ The methods of the `KgBuilder` class can be chained together to perform a
sequence of operations.
-The methods of the `KgBuilder` class can be chained together to perform a
sequence of operations.
-
-### 2. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) based on HugeGraph
+### 4.2 Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) based on HugeGraph
The `RAGPipeline` class is used to integrate HugeGraph with large language
models to provide retrieval-augmented generation capabilities.
Here is a brief usage guide:
1. **Extract Keyword**: Extract keywords and expand synonyms.
-
```python
from hugegraph_llm.operators.graph_rag_task import RAGPipeline
graph_rag = RAGPipeline()
graph_rag.extract_keywords(text="Tell me about Al Pacino.").print_result()
```
-
-2. **Match Vid from Keywords*: Match the nodes with the keywords in the graph.
-
+2. **Match Vid from Keywords**: Match the nodes with the keywords in the graph.
```python
graph_rag.keywords_to_vid().print_result()
```
-
3. **Query Graph for Rag**: Retrieve the corresponding keywords and their
multi-degree associated relationships from HugeGraph.
-
```python
graph_rag.query_graphdb(max_deep=2, max_items=30).print_result()
```
-
4. **Rerank Searched Result**: Rerank the searched results based on the
similarity between the question and the results.
-
```python
graph_rag.merge_dedup_rerank().print_result()
```
-
5. **Synthesize Answer**: Summarize the results and organize the language to
answer the question.
-
```python
graph_rag.synthesize_answer(vector_only_answer=False,
graph_only_answer=True).print_result()
```
-
6. **Run**: The `run` method is used to execute the above operations.
-
```python
graph_rag.run(verbose=True)
```
