This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
kimmking pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/shardingsphere.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 47322ac translate the solution from solution.cn.md to solution.en.md
(#6229)
47322ac is described below
commit 47322ac7074df09bf13d345036e99988b8e3088b
Author: mlw12345678 <40895047+mlw12345...@users.noreply.github.com>
AuthorDate: Thu Jul 2 16:37:18 2020 +0800
translate the solution from solution.cn.md to solution.en.md (#6229)
---
docs/blog/content/material/solution.en.md | 250 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++-
1 file changed, 249 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
diff --git a/docs/blog/content/material/solution.en.md
b/docs/blog/content/material/solution.en.md
index 1d51f1d..3cc60ab 100644
--- a/docs/blog/content/material/solution.en.md
+++ b/docs/blog/content/material/solution.en.md
@@ -4,4 +4,252 @@ weight = 9
chapter = true
+++
-## TODO
+## The mixed open-source distributed transaction solution
+
+### Author
+
+Liang Zhang,Head of Data R&D of JD.com, initiator of Apache ShardingSphere &
PPMC
+
+Love open source, currently leading open source projects ShardingSphere
(formerly known as Sharding-JDBC) and Elastic-Job. Good at using Java as the
main distributed architecture and Kubernetes and Mesos as the main cloud
platform, admiring elegant code, and having more research on how to write
expressive code.
+
+At present, the main energy is invested in building ShardingSphere into the
industry's first-class financial data solution. ShardingSphere has entered the
Apache incubator, is the first open source project of the Jingdong Group to
enter the Apache Foundation, and is also the first distributed database
middleware of the Apache Foundation.
+
+---
+Ning Jiang,Technical expert of Huawei Open Source Competency Center, project
leader of Apache ServiceComb. Former chief software engineer of Red Hat
Software, he has more than ten years of experience in enterprise-level open
source middleware development, rich experience in Java development and use, and
he also is the enthusiast of functional programming. Since 2006, he has been
engaged in the development of the Apache open source middleware project, and
has participated in the developme [...]
+
+Blog address:https://willemjiang.github.io/
+
+---
+
+Zheng Feng is a software engineer at Red Hat. Joined Red Hat Software in 2009,
mainly engaged in the work of the transaction manager. As a core developer, he
participated in the Narayan and Blacktie projects. He had contributed to the
integration of transaction processing of multiple application servers (Wildfly,
Karaf, Tomcat) and frameworks (Common DBCP, Spring Boot ). Since 2017, he has
participated in the Apache ServiceComb project and is currently a member of
PMC. He has in-depth re [...]
+
+### Guide
+
+Compared with the gradual maturity of data sharding solutions, distributed
transaction solutions that combine performance, transparency, automation,
strong consistency, and can be applied to various application scenarios in one
are very rare. Based on the performance bottlenecks of distributed transactions
submitted in two (three) stages and the business transformation of flexible
transactions, distributed transactions are still a headache for architects.
+
+At the beginning of 2019, Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) provided a rigid
and flexible integrated distributed transaction solution. If your application
system is being troubled by this aspect, why not pour a cup of coffee and spend
ten minutes reading this article, maybe you will gain something?
+
+### Background
+
+Database transactions need to meet the four characteristics of ACID
(Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability).
+
+- Atomicity Refers to the execution of the transaction as a whole, either
all or no execution.
+
+- Consistency Refers to the transaction should ensure that the data changes
from one consistent state to another consistent state.
+
+- Isolation When multiple transactions are executed concurrently, the
execution of one transaction should not affect the execution of other
transactions.
+
+- Durability Refers to the committed transaction modification data will be
persisted.
+
+In a single data node, the transaction is limited to the access control of a
single database resource, called local transaction. Almost all mature
relational databases provide native support for local transactions. However, in
a distributed application environment based on microservices, more and more
application scenarios require that access to multiple services and
corresponding multiple database resources can be incorporated into the same
transaction, then the distributed transactions [...]
+
+Although the relational database provides perfect ACID native support for
local transactions. But in a distributed scenario, it has become a shackle in
system performance. How to make the database meet the characteristics of ACID
or find corresponding alternatives in a distributed scenario is the focus of
distributed transactions.
+
+#### Local transaction
+
+Without opening any distributed transaction manager, let each data node manage
its own transaction. There is no coordination and communication between them,
and they do not know each other's success of other data node transactions.
There is no loss in performance for local transactions, but it is inadequate in
terms of strong consistency and eventual consistency.
+
+#### Two-phase commit
+
+The earliest distributed transaction model of the XA protocol is the X/Open
Distributed Transaction Processing (DTP) model proposed by the X/Open
International Alliance, referred to as the XA protocol.
+
+The distributed transaction based on the XA protocol has little intrusion on
the business. Its biggest advantage is that it is transparent to the user.
Users can use distributed transactions based on the XA protocol like local
transactions. The XA protocol can strictly guarantee the ACID characteristics
of transactions.
+
+Strictly guaranteeing ACID characteristics of transactions is a double-edged
sword. In the process of transaction execution, all required resources need to
be locked, so the XA protocol is more suitable for short transactions whose
execution time is determined. For long transactions, the exclusive use of data
during the entire transaction will cause the concurrency performance of
business systems that rely on hot data to decline significantly. Therefore, in
high-concurrency performance-o [...]
+
+#### Flexible transaction
+
+If the transaction that implements the ACID transaction element is called a
rigid transaction, the transaction based on the BASE transaction element is
called a flexible transaction. BASE is an abbreviation of the three elements of
basic availability, flexible state and final consistency.
+
+- Basically Available Ensure that participants in distributed transactions
are not necessarily online at the same time.
+
+- Soft state It allows a certain delay in the system status update, and this
delay may not be noticeable to customers.
+
+- Eventually consistent Usually, the final consistency of the system is
ensured by means of message passing.
+
+In ACID transactions, the requirements for consistency and isolation are very
high. During the execution of the transaction, all resources must be occupied.
The idea of flexible transactions is to move the mutex operation from the
resource level to the business level through business logic. By relaxing the
requirements for strong consistency and isolation, only when the entire
transaction ends, the data is consistent. During the execution of the
transaction, any data obtained by the read [...]
+
+Saga is a typical flexible transaction manager. The concept of Sagas comes
from a database paper more than thirty years ago
[http://www.cs.cornell.edu/andru/cs711/2002fa/reading/sagas.pdf], a Saga
transaction is A long-term transaction which is composed of multiple short-term
transactions. In the distributed transaction scenario, we regard a Saga
distributed transaction as a transaction composed of multiple local
transactions, and each local transaction has a corresponding compensation t
[...]
+
+TCC (Try-Cancel/Confirm implementation) is another kind of flexible
transaction coordination implementation. TCC provides a more perfect recovery
method with the help of a two-phase submission agreement. In TCC mode, cancel
compensation obviously needs to execute business logic in the second stage to
cancel the consequences of the first stage. Try is to perform related business
operations in the first stage to complete the occupation of related business
resources, such as pre-allocating [...]
+
+The strong consistency transaction based on ACID and the final consistency
transaction based on BASE are not silver bullets, and their greatest strengths
can only be used in the most suitable scenarios. The following table can be
used to compare the differences between them in detail to help developers
choose technologies.
+
+<center>
+
+
+| Contrast | Local Transaction |
Two-phase Submission | Flexible Transaction |
+| :---------------------: | :---------------------------------------: |
:---------------------------------: | :---------------------------------: |
+| Business Transformation | No need |
No need | Implement related interfaces |
+| Consistency | Not support |
Support | Final consistency |
+| Isolation | Not support |
Support | Business guarantee |
+| Concurrent Performance | No effect |
Severe decline | Slight decline |
+| Suitable Scenarios | Inconsistent processing by business party | Short
transaction & Low concurrency | Long transaction & High concurrency |
+
+</center>
+
+#### Challenge
+
+Due to different application scenarios, developers need to be able to
reasonably choose various distributed transactions between performance and
functionality.
+
+The API and functions of the two-phase commit and flexible transactions are
not exactly the same, and there is no free and transparent switching between
them. In the development decision-making stage, you have to choose between
transactions submitted in two stages and flexible transactions, which greatly
increases the cost of design and development.
+
+The XA-based two-phase commit transaction is relatively simple to use, but it
cannot deal well with the Internet's high concurrency or long transaction
scenarios of complex systems; flexible transactions require developers to
transform applications, access costs are very high, and developers are required
Implement resource occupancy and reverse compensation on your own.
+
+### Distributed transactions of ShardingSphere
+
+Integrate existing mature transaction solutions, provide a unified distributed
transaction interface for local transactions, two-phase commit and flexible
transactions, and make up for the shortcomings of the current solution, the
main design goal of the Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) distribution
transactional module is providing a one-stop distributed transaction solution.
The name of the module is sharding-transaction. The three key words of
combination of hardness and softness, a [...]
+
+1.The combination of hardness and softness
+
+At the same time provide XA-based two-phase commit transaction and Saga-based
flexible transaction solution, and can be used together.
+
+2.Automation
+
+XA transactions and Saga transactions are completed in an automated manner,
and the user has no awareness. XA transactions do not require the use of
XADataSource interface and JTA transaction manager; Saga transactions also do
not require users to implement compensation interfaces themselves.
+
+3.Transparency
+
+In the two access points of Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating), Sharding-JDBC
and Sharding-Proxy, respectively provide the encapsulation for the local
transaction interface. The user can fully use the multiple data sources of
horizontal sharding managed by ShardingSphere as one database, and the complete
distributed transaction capability can be achieved through the local
transaction API. Users can transparently switch transaction types in the
application.
+
+The sharding-transaction module consists of three sub-modules:
sharding-transaction-core, sharding-transaction-2pc and
sharding-transaction-base.
+
+- sharding-transaction-core:
+
+Provides APIs for users and SPIs for developers.
+
+- sharding-transaction-2pc:
+
+The parent module of two-stage commit transaction. Currently only the
sharding-transaction-xa module provides XA protocol support. In the future,
more types of transactions based on two-phase commit will be introduced, such
as: percolator, see:
+
+[https://storage.googleapis.com/pub-tools-public-publication-data/pdf/36726.pdf]。
+
+- sharding-transaction-base:
+
+The parent module of flexible transaction. Currently, there is only the
sharding-transaction-saga module, which uses the Saga executor provided by
Apache ServiceComb Saga Actuator to provide flexible transaction support, and
on the basis of it provides reverse SQL and snapshot capabilities, and thus
realizes automatic reverse compensation.
+
+The function highlights of ShardingSphere's XA and Saga transaction modules
will be described below.
+
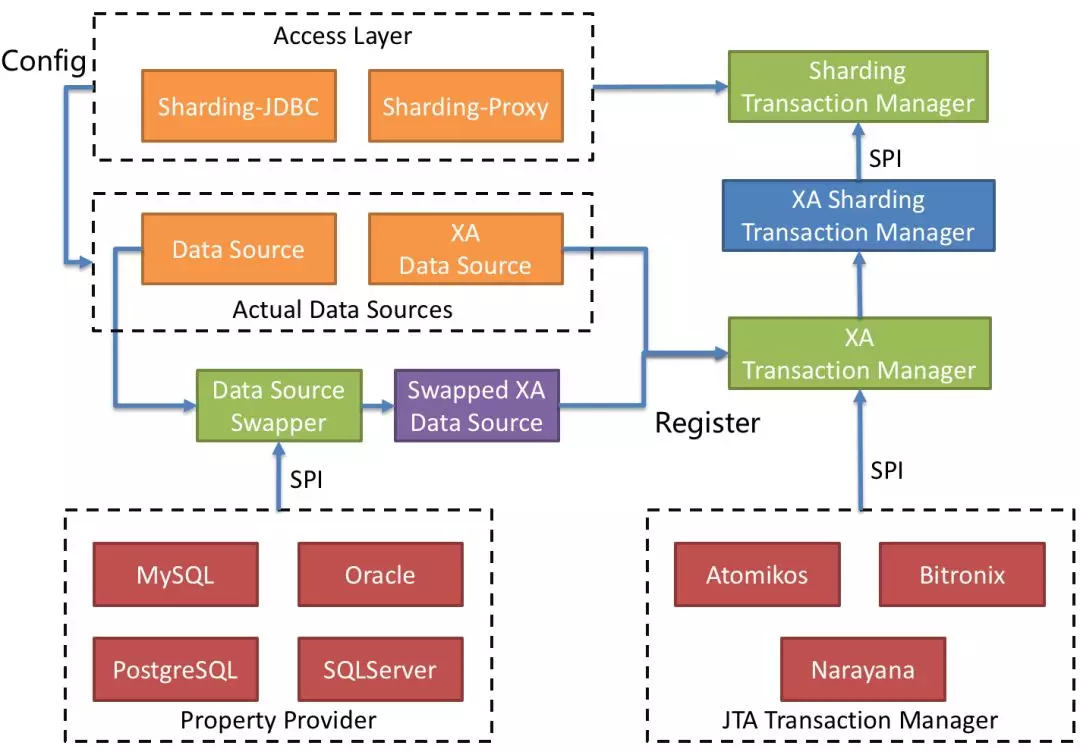
+#### XA transaction-three XA transaction managers escort together
+
+There are many mature XA transaction managers. Apache ShardingSphere
(Incubating) did not choose to reinvent the wheel. Instead, it hoped to create
an ecology that organically integrates the appropriate wheels to provide mature
and stable distributed transaction processing capabilities. Its main functions
are as follows:
+
+**1.Reuse mature engine, automatically switch the underlying implementation**
+
+The Sharding-transaction-xa module further defines the SPI for XA transaction
manager developers. Developers only need to implement the SPI-defined interface
to automatically join the Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) ecosystem as their
XA transaction manager.
+
+Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) officially implements SPI based on Atomikos
and Bitronix, and invited the Radhat JBoss XA transaction engine Narayana
[https://github.com/jbosstm/narayana] development team to implement JBoss SPI.
Users can choose their favorite XA transaction manager among Atomikos, Bitronix
and Narayana.
+
+
+
+Limited by the license of the Apache Foundation project, Apache ShardingSphere
(Incubating) uses Atomikos of the Apache protocol as its default
implementation. Regarding Bitronix based on the LGPL protocol and Narayana
based on the LGPL protocol, users can refer to the corresponding jar package to
the classpath of project.
+
+
+
+If these three XA transaction managers still do not meet user needs,
developers can implement customized XA transaction managers by extending SPI.
+
+
+
+**2.Automatic access to transparent data sources**
+
+
+
+Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) can automatically connect XADataSource as a
database-driven data source to the XA transaction manager. For applications
that use DataSource as a database driver, users do not need to change their
encoding and configuration. Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) converts it into
XADataSource and XAConnection that support the XA protocol through automatic
adaptation. It is registered as an XA resource in the underlying XA transaction
manager.
+
+
+
+The architecture diagram of the XA module is as follows:
+
+
+
+
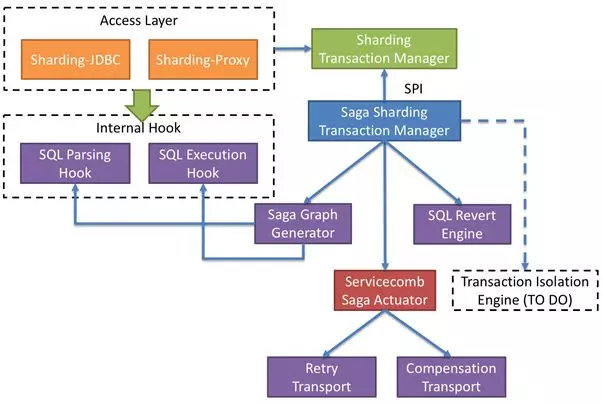
+#### Saga transactions—overcome the limitations of flexible transactions and
realize automatic compensation
+
+In flexible transactions, each update operation to the database will actually
submit the data to the database to achieve the best resource release effect in
a highly concurrent system. When data needs to be rolled back, the flexible
transaction manager maintains the final consistency of the data and the
isolation behavior. Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) uses Apache ServiceComb
Saga Actuator [https://github.com/apache/servicecomb-saga-actuator] as the Saga
transaction manager. Its mai [...]
+
+
+
+**1. Automatic reverse compensation**
+
+
+
+Saga defines that each sub-transaction in a transaction has a corresponding
reverse compensation operation. The Saga transaction manager generates a
directed acyclic graph based on the program execution results, and when the
rollback operation needs to be performed, reverse compensation operations are
called in reverse order according to the graph. The Saga transaction manager is
only used to control when to retry, appropriate compensation, and is not
responsible for the content of compe [...]
+
+
+
+Another flexible transaction manager, TCC, is similar to the Saga concept, and
both require compensation operations from the user developer. In addition to
compensation, TCC also provides the ability to occupy resources, but it also
needs to be provided by the developer of the user. Although functionally
stronger than Saga, the cost of using TCC is also higher than that of Saga.
+
+
+
+The user developer provides resource occupancy and compensation operations,
which makes it difficult for flexible transaction solutions to be implemented
in business systems on a large scale. And because of the intervention of the
business system, the use scope of the flexible transaction framework has always
been positioned as a service rather than a database. The mature flexible
transaction manager that the database can directly use is still rare.
+
+
+
+Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) uses reverse SQL technology to
automatically generate data snapshots and reverse SQL for the SQL that updates
the database, and it is executed by Apache ServiceComb Saga Actuator. The user
does not need to pay attention to how to implement the compensation method. The
application category of the transaction manager is successfully positioned back
to the source of the transaction -- the database level.
+
+
+
+For the Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) SQL parsing engine that can process
complex query statements, the difficulty of parsing statements such as
insert/update/delete is much smaller; ShardingSphere intercepts the SQL
executed by the user to perform data sharding. All SQL Can be directly
controlled by it. Therefore, the combination of reverse SQL and compensation
capabilities with Apache ServiceComb Saga Actuator achieves the ability to
automate flexible transactions, which is a mode [...]
+
+
+
+The architecture diagram of the Saga module is as follows:
+
+
+
+#### Access point -- Distributed transaction for native transaction interface
+
+The goal of Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) is to use sharded
multi-database like a database. In the transaction module, this goal is still
applicable. No matter how fragmented the database managed by ShardingSphere,
there is always only one logical database for developers. Therefore,
ShardingSphere's transaction interface is still the native local transaction
interface, namely the setAutoCommit, commit and rollback methods of JDBC's
java.sql.Connection; and the begin, commit and roll [...]
+
+
+
+Since the native transaction interface does not support transaction types,
ShardingSphere provides 3 ways for users to switch transaction types.
+
+
+
+1.Switch the current transaction type through SCTL (sharding-ctl, the database
management command provided by ShardingSphere). Just enter it in SQL execution
mode, and it is applicable to Sharding-JDBC and Sharding-Proxy. For example:
SCTL:SET TRANSACTION_TYPE=BASE
+
+2.Switch the current transaction type through Threadlocal, suitable for
Sharding-JDBC. For example: TransactionTypeHolder.set (TransactionType.XA)
+
+3.Through meta-annotation, and used with Spring to switch the current
transaction type, suitable for Sharding-JDBC and Sharding-Proxy. For example:
@ShardingTransactionType (TransactionType.BASE)
+
+### Future plan
+
+The distributed transaction module in the development branch of github
[https://github.com/apache/incubator-shardingsphere] is basically available and
will be released with the version of 4.0.0.M1, which will also be the first
release version when ShardingSphere into the Apache Foundation incubator.
Distributed transactions are an important part of data sharding and
microservice architecture. They are also the focus of Apache ShardingSphere
(Incubating). After the release, they will cont [...]
+
+#### Transaction isolation engine
+
+After the SQL reverse engine is stabilized, the focus of flexible transactions
will be on creating transaction isolation. Since the isolation of transactions
is not the scope of Saga's plan, Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) will
improve it outside of Saga, together with the SQL reverse engine as an integral
part of the entire flexible transaction.
+
+
+
+Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating) will support the isolation level of read
committed, read uncommitted, repeatable read, and serialization through several
strategies such as optimistic locking, pessimistic locking, and no isolation.
And through the multi-version snapshot to further improve the concurrency of
the system.
+
+#### External XA transaction interface
+
+The two access ends of Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating), Sharding-JDBC and
Sharding-Proxy, after supporting their own internal transaction issues, will
provide the ability to integrate with other data sources to be managed by
distributed transaction manager such as JTA.
+
+
+
+After the external XA transaction interface is implemented, the Sharding-JDBC
DataSource will implement the XADataSource interface, providing the possibility
to join with other data sources in an XA transaction; Sharding-Proxy's database
protocol will also implement a two-stage XA-based submission protocol; Let it
become the resource manager loaded by XA.
+
+
+
+In addition, ShardingSphere will also implement the recovery part of the XA
protocol, that is, when the transaction processor crashes, it can provide
in-doubt transactions to achieve transaction recovery.
+
+
+### summary
+
+The distributed transaction capabilities provided by Apache ShardingSphere
(Incubating) can be summarized by the following table. Readers may wish to
compare with the table at the beginning of the article to see the changes
brought by ShardingSphere's distributed transaction module.
+
+
+| Contrast | Local Transaction |
Two-phase Submission | Flexible Transaction |
+| :---------------------: | :---------------------------------------: |
:---------------------------------: | :---------------------------------: |
+| Business Transformation | No need |
No need | <font color=#ff0000>No need</font> |
+| Consistency | Not support |
Support | Final consistency |
+| Isolation | Not support |
Support | <font color=#ff0000>Planning</font> |
+| Concurrent Performance | No effect |
Severe decline | Slight decline |
+| Suitable Scenarios | Inconsistent processing by business party | Short
transaction & Low concurrency | Long transaction & High concurrency |
+
+In the fast-developing Apache ShardingSphere (Incubating), the prototype of
distributed transactions has been established. We will build it into a usable
product as soon as possible and continue to provide quality solutions to the
community. For an article that is not short, after reading this article, I
believe you must be interested in this field. Let’s try it first. Does it meet
your expectations? Or simply join our community to create a more complete
distributed transaction solution.
+
