This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
zhaojinchao pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/shardingsphere.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new c38adb0c9ef Refactor doc in features shadow (#18717)
c38adb0c9ef is described below
commit c38adb0c9ef6a7513c1f2722a46cb13e7e4500f3
Author: gin <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Thu Jun 30 11:08:29 2022 +0800
Refactor doc in features shadow (#18717)
---
docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.cn.md | 87 ++++++++++++++++-----
docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.en.md | 85 ++++++++++++++------
.../document/content/features/shadow/concept.cn.md | 26 ------
.../document/content/features/shadow/concept.en.md | 26 ------
.../content/features/shadow/use-norms.cn.md | 41 ----------
.../content/features/shadow/use-norms.en.md | 41 ----------
docs/document/static/img/shadow/execute.png | Bin 70280 -> 115979 bytes
7 files changed, 132 insertions(+), 174 deletions(-)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.cn.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.cn.md
index 46b7248b759..7f9ea8a6286 100644
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.cn.md
+++ b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.cn.md
@@ -1,27 +1,78 @@
+++
-pre = "<b>4.10. </b>"
-title = "影子库压测"
-weight = 10
-chapter = true
+pre = "<b>7.6. </b>"
+title = "影子库"
+weight = 6
+++
-## 背景
+## 定义
+Apache ShardingSphere 全链路在线压测场景下,在数据库层面对于压测数据治理的解决方案。
-在基于微服务的分布式应用架构下,业务需要多个服务是通过一系列的服务、中间件的调用来完成,所以单个服务的压力测试已无法代表真实场景。
-在测试环境中,如果重新搭建一整套与生产环境类似的压测环境,成本过高,并且往往无法模拟线上环境的复杂度以及流量。
-因此,业内通常选择全链路压测的方式,即在生产环境进行压测,这样所获得的测试结果能够准确地反应系统真实容量和性能水平。
+## 相关概念
-## 挑战
+### 生产库
+生产环境使用的数据库。
-全链路压测是一项复杂而庞大的工作。
-需要各个微服务、中间件之间配合与调整,以应对不同流量以及压测标识的透传。
-通常会搭建一整套压测平台以适用不同测试计划。
-在数据库层面需要做好数据隔离,为了保证生产数据的可靠性与完整性,需要将压测产生的数据路由到压测环境数据库,防止压测数据对生产数据库中真实数据造成污染。
-这就要求业务应用在执行 SQL 前,能够根据透传的压测标识,做好数据分类,将相应的 SQL 路由到与之对应的数据源。
+### 影子库
+压测数据隔离的影子数据库,与生产数据库应当使用相同的配置。
-## 目标
+### 影子算法
+影子算法和业务实现紧密相关,目前提供 2 种类型影子算法。
-**Apache ShardingSphere 关注于全链路压测场景下,数据库层面的解决方案。
-将压测数据自动路由至用户指定的数据库,是 Apache ShardingSphere 影子库模块的主要设计目标。**
+- 基于列的影子算法
+ 通过识别 SQL 中的数据,匹配路由至影子库的场景。
+ 适用于由压测数据名单驱动的压测场景。
+
+- 基于 Hint 的影子算法
+ 通过识别 SQL 中的注释,匹配路由至影子库的场景。
+ 适用于由上游系统透传标识驱动的压测场景。
+
+## 使用限制
-**源码:https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere/tree/master/shardingsphere-features/shardingsphere-shadow**
+### 基于 Hint 的影子算法
+* 无。
+
+### 基于列的影子算法
+* 不支持 DDL;
+* 不支持范围、分组和子查询,如:BETWEEN、GROUP BY ... HAVING 等。
+ SQL 支持列表:
+ - INSERT
+
+ | *SQL* | *是否支持* |
+ | ------- | ------------ |
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...) | 支持 |
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...),(value,...),... | 支持
|
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) SELECT column1 from table1 where column1 =
value1 | 不支持 |
+
+ - SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE
+
+ | *条件类型* | *SQL* | *是否支持* |
+ | ------------ | -------- | ----------- |
+ | = | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = value | 支持 |
+ | LIKE/NOT LIKE | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column LIKE/NOT LIKE value
| 支持 | | IN/NOT IN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE
column IN/NOT IN (value1,value2,...) | 支持 |
+ | BETWEEN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column BETWEEN value1 AND value2
| 不支持 |
+ | GROUP BY ... HAVING... | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE ... GROUP BY
column HAVING column > value | 不支持 |
+ | 子查询 | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = (SELECT column FROM table
WHERE column = value) | 不支持 |
+
+## 原理介绍
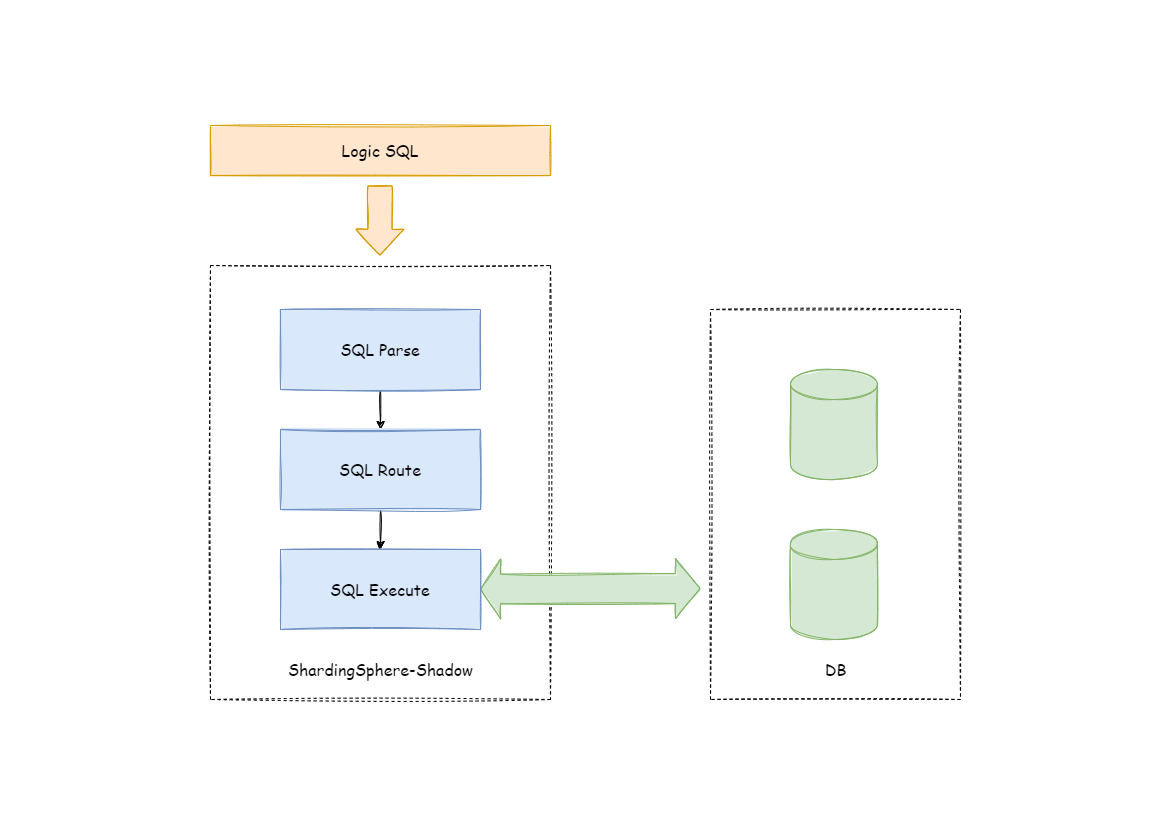
+Apache ShardingSphere 通过解析 SQL,对传入的 SQL 进行影子判定,根据配置文件中用户设置的影子规则,路由到生产库或者影子库。
+
+
+以 INSERT 语句为例,在写入数据时,Apache ShardingSphere 会对 SQL 进行解析,再根据配置文件中的规则,构造一条路由链。
在当前版本的功能中,影子功能处于路由链中的最后一个执行单元,即,如果有其他需要路由的规则存在,如分片,Apache ShardingSphere
会首先根据分片规则,路由到某一个数据库,再执行影子路由判定流程,判定执行SQL满足影子规则的配置,数据路由到与之对应的影子库,生产数据则维持不变。
+
+### DML 语句
+支持两种算法。影子判定会首先判断执行 SQL 相关表与配置的影子表是否有交集。如果有交集,依次判定交集部分影子表关联的影子算法,有任何一个判定成功。SQL
语句路由到影子库。
+影子表没有交集或者影子算法判定不成功,SQL 语句路由到生产库。
+
+### DDL 语句
+仅支持注解影子算法。在压测场景下,DDL 语句一般不需要测试。主要在初始化或者修改影子库中影子表时使用。
+影子判定会首先判断执行 SQL 是否包含注解。如果包含注解,影子规则中配置的 HINT 影子算法依次判定。有任何一个判定成功。SQL 语句路由到影子库。
+执行 SQL 不包含注解或者 HINT 影子算法判定不成功,SQL 语句路由到生产库。
+
+## 相关参考
+[JAVA API:影子库配置](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/java-api/rules/shadow/)
+
+[YAML 配置:影子库配置](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/yaml-config/rules/shadow/)
+
+[ Spring Boot Starter:影子库配置
](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-boot-starter/rules/shadow/)
+
+[Spring
命名空间:影子库配置](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-namespace/rules/shadow/)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.en.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.en.md
index 51131f85ff1..bab8ad8cece 100644
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.en.md
+++ b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/_index.en.md
@@ -1,36 +1,77 @@
+++
-pre = "<b>4.10. </b>"
-title = "Shadow DB"
-weight = 10
-chapter = true
+pre = "<b>7.6. </b>"
+title = "Shadow"
+weight = 6
+++
-## Background
+## Definition
+Solution for stress testing data governance at the database level, under the
online full link stress testing scenario of Apache Shardingsphere.
-Under the distributed application architecture based on microservices,
business requires multiple services to be completed through a series of
services and middleware calls.
-The pressure testing of a single service can no longer reflect the real
scenario.
+## Related Concepts
-In the test environment, the cost of rebuild complete set of pressure test
environment similar to the production environment is too high.
-It is usually impossible to simulate the complexity and data of the production
environment.
+### Production Database
+Database for production data
-So, it is the better way to use the production environment for pressure test.
-The test results obtained real capacity and performance of the system
accurately.
+### Shadow Database
+The Database for stress test data isolation. Configurations should be the same
as the Production Database.
-## Challenges
+### Shadow Algorithm
+Shadow Algorithm, which is closely related to business operations, currently
has 2 types.
-pressure testing on production environment is a complex and huge task.
-Coordination and adjustments between microservices and middlewares required to
cope with the transparent transmission of different flow rates and pressure
test tags.
-Usually we will build a complete set of pressure testing platform for
different test plans.
+- Column based shadow algorithm
+Routing to shadow database by recognizing data from SQL. Suitable for stress
test scenario that has an emphasis on data list.
+- Hint based shadow algorithm
+Routing to shadow database by recognizing comments from SQL. Suitable for
stress test driven by the identification of upstream system passage.
-Data isolation have to be done at the database-level, in order to ensure the
reliability and integrity of the production data, data generated by pressure
testing routed to test database.
-Prevent test data from polluting the real data in the production database.
+## Limitations
-This requires business applications to perform data classification based on
the transparently transmitted pressure test identification before executing
SQL, and route the corresponding SQL to the corresponding data source.
+### Hint based shadow algorithm
+No
-## Goal
+### Column based shadow algorithm
+Does not support DDL.
+Does not support scope, group, subqueries such as BETWEEN, GROUP BY ...
HAVING, etc.
+SQL support list
-**Apache ShardingSphere focuses on data solutions in pressure testing on
production environment.
+ - INSERT
+
+ | *SQL* | *support or not* |
+ | ------- | ------------ |
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...) | support |
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...),(value,...),... |
support |
+ | INSERT INTO table (column,...) SELECT column1 from table1 where column1 =
value1 | do not support |
+ - SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE
+
+ | *condition categories* | *SQL* | *support or not* |
+ | ------------ | -------- | ----------- |
+ | = | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = value | support |
+ | LIKE/NOT LIKE | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column LIKE/NOT LIKE value
| support | | IN/NOT IN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ...
WHERE column IN/NOT IN (value1,value2,...) | support |
+ | BETWEEN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column BETWEEN value1 AND value2
| do not support |
+ | GROUP BY ... HAVING... | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE ... GROUP BY
column HAVING column > value | do not support |
+ | Sub Query | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = (SELECT column FROM
table WHERE column = value) | do not support |
-The main goal of the Apache ShardingSphere shadow Database module is routing
pressure testing data to user defined database automatically.**
+## How it works
-**Source Codes:
https://github.com/apache/shardingsphere/tree/master/shardingsphere-features/shardingsphere-shadow**
+Apache ShardingSphere determines the incoming SQL via shadow by parsing the
SQL and routing it to the production or shadow database based on the shadow
rules set by the user in the configuration file.
+
+
+In the example of an INSERT statement, when writing data, Apache
ShardingSphere parses the SQL and then constructs a routing chain based on the
rules in the configuration file.
+In the current version, the shadow feature is at the last execution unit in
the routing chain, i.e. if other rules exist that require routing, such as
sharding, Apache ShardingSphere will first route to a particular database
according to the sharding rules, and then run the shadow routing determination
process to determine that the execution SQL meets the configuration set by
shadow rules. Then data is routed to the corresponding shadow database, while
the production data remains unchanged.
+
+### DML sentence
+Two algorithms are supported. Shadow determination first determines whether
the execution SQL-related table intersects with the configured shadow table. If
the result is positive, the shadow algorithm within the part of intersection
associated with the shadow table will be determined sequentially. If any of the
determination is successful, the SQL statement is routed to the shadow library.
+If there is no intersection or the shadow algorithm determination is
unsuccessful, the SQL statement is routed to the production database.
+
+### DDL sentence
+Only supports shadow algorithm with comments attached. In stress testing
scenarios, DDL statements are generally not required for testing, and are used
mainly when initializing or modifying shadow tables in the shadow database.
+The shadow determination will first determine whether the execution SQL
contains comments or not. If the result is a yes, the HINT shadow algorithm
configured in the shadow rules determines them in order. The SQL statement is
routed to the shadow database if any of the determinations are successful.
+If the execution SQL does not contain comments or the HINT shadow algorithm
determination is unsuccessful, the SQL statements are routed to the production
database.
+
+## References
+[JAVA API: shadow database
configuration](/en/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/java-api/rules/shadow/)
+
+[YAML Configuration: shadow
database](/en/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/yaml-config/rules/shadow/)
+
+[ Spring Boot Starter: shadow database
configuration](/en/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-boot-starter/rules/shadow/)
+
+[Spring namespace: shadow database
configuration](/en/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-namespace/rules/shadow/)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.cn.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.cn.md
deleted file mode 100644
index e713ffcb2c0..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.cn.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "核心概念"
-weight = 1
-+++
-
-## 生产库
-
-生产环境使用的数据库。
-
-## 影子库
-
-压测数据隔离的影子数据库,与生产数据库应当使用相同的配置。
-
-## 影子算法
-
-影子算法和业务实现紧密相关,目前提供 2 种类型影子算法。
-
-- 基于列的影子算法
-
-通过识别 SQL 中的数据,匹配路由至影子库的场景。
-适用于由压测数据名单驱动的压测场景。
-
-- 基于 Hint 的影子算法
-
-通过识别 SQL 中的注释,匹配路由至影子库的场景。
-适用于由上游系统透传标识驱动的压测场景。
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.en.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.en.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 57999d1c7b4..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/concept.en.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "Core Concept"
-weight = 1
-+++
-
-## Production Database
-
-The database used for production data.
-
-## Shadow Database
-
-The database for pressure testing data isolation.
-
-## Shadow Algorithm
-
-The shadow algorithms are closely related to business, there are 2 types of
shadow algorithms provided.
-
-- Column based shadow algorithm
-
-Recognize data from SQL and route to shadow databases.
-Suitable for test data driven scenario.
-
-- Hint based shadow algorithm
-
-Recognize comment from SQL and route to shadow databases.
-Suitable for identify passed by upstream system scenario.
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.cn.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.cn.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d6003cad94..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.cn.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "使用规范"
-weight = 2
-+++
-
-## 支持项
-
-* 基于 Hint 的影子算法支持全部 SQL;
-* 基于列的影子算法仅支持部分 SQL。
-
-## 不支持项
-
-### 基于 Hint 的影子算法
-
-* 无。
-
-### 基于列的影子算法
-
-* 不支持 DDL;
-* 不支持范围、分组和子查询,如:BETWEEN、GROUP BY ... HAVING 等。
-
-SQL 支持列表:
-
-- INSERT
-
-| *SQL*
| *是否支持* |
-|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| --------- |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...)
| 支持 |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...),(value,...),...
| 支持 |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) SELECT column1 from table1 where column1 =
value1 | 不支持 |
-
-- SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE
-
-| *条件类型* | *SQL*
| *是否支持* |
-| ---------------------- |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| --------- |
-| = | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = value
| 支持 |
-| LIKE/NOT LIKE | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column LIKE/NOT LIKE
value | 支持 |
-| IN/NOT IN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column IN/NOT IN
(value1,value2,...) | 支持 |
-| BETWEEN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column BETWEEN
value1 AND value2 | 不支持 |
-| GROUP BY ... HAVING... | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE ... GROUP BY column
HAVING column > value | 不支持 |
-| 子查询 | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = (SELECT
column FROM table WHERE column = value) | 不支持 |
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.en.md
b/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.en.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 0b3457a6fde..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/shadow/use-norms.en.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "Use Norms"
-weight = 2
-+++
-
-## Supported
-
-* Hint based shadow algorithm support all SQL;
-* Column based shadow algorithm support part of SQL.
-
-## Unsupported
-
-### Hint based shadow algorithm
-
-* None
-
-### Column based shadow algorithm
-
-* Does not support DDL;
-* Does not support range, group and subquery, for example: BETWEEN, GROUP BY
... HAVING...;
-
-SQL support list:
-
-- INSERT
-
-| *SQL*
| *Supported* |
-|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| ------------ |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...)
| Y |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) VALUES (value,...),(value,...),...
| Y |
-| INSERT INTO table (column,...) SELECT column1 from table1 where column1 =
value1 | N |
-
-- SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE
-
-| *Condition* | *SQL*
| *Supported* |
-| ---------------------- |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| ----------- |
-| = | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = value
| Y |
-| LIKE/NOT LIKE | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column LIKE/NOT LIKE
value | Y |
-| IN/NOT IN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column IN/NOT IN
(value1,value2,...) | Y |
-| BETWEEN | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column BETWEEN
value1 AND value2 | N |
-| GROUP BY ... HAVING... | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE ... GROUP BY column
HAVING column > value | N |
-| Subquery | SELECT/UPDATE/DELETE ... WHERE column = (SELECT
column FROM table WHERE column = value) | N |
diff --git a/docs/document/static/img/shadow/execute.png
b/docs/document/static/img/shadow/execute.png
index bd9179cb37d..f9a027bec2c 100644
Binary files a/docs/document/static/img/shadow/execute.png and
b/docs/document/static/img/shadow/execute.png differ
